What Makes Up a Horse's Anatomy and Physiology?
If you've ever marveled at the majestic grace of a horse galloping across a field, have you ever considered what lies beneath that powerful exterior?
From the elegant curve of their neck to the sturdy hooves that carry them, a horse's anatomy and physiology are a symphony of intricate systems working in harmony.
As you explore the skeletal framework that supports their every movement and the complex network of muscles propelling them forward, you'll begin to unravel the fascinating world of these magnificent creatures.
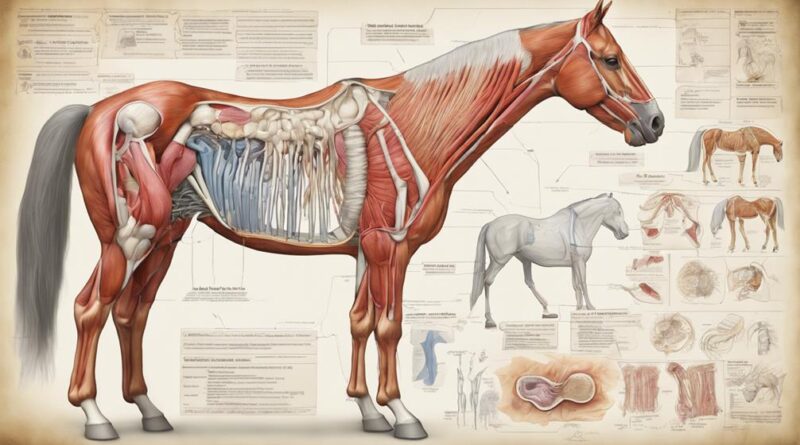
Skeletal System
Understanding the structure of the horse's skeletal system is essential for grasping its functionality and overall health. The bone structure of a horse is a marvel of engineering, providing support, protection, and mobility. The horse's skeleton is made up of around 205 bones, with each bone serving a specific purpose in maintaining the horse's form and enabling movement.
When considering bone structure, it's crucial to recognize that a horse's bones aren't only strong but also lightweight. This combination is vital for the horse's ability to move swiftly and gracefully. The bones are connected at joints, allowing for different types of movement. Joint movement in horses is crucial for their agility and speed. Horses have three main types of joints: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. The synovial joints, which are the most common in horses, allow for a wide range of movements due to their structure and the presence of synovial fluid.
As you observe a horse in motion, pay attention to how its bones and joints work together seamlessly. The intricate coordination between bone structure and joint movement is what enables the horse to gallop, jump, and maneuver with precision. By understanding the skeletal system's role in supporting the horse's movements, you can better appreciate the incredible athleticism and grace of these magnificent animals.
Muscular System
The muscular system of a horse consists of over 700 individual muscles working in harmony to facilitate movement and provide strength and power. These muscles play a crucial role in the horse's ability to run, jump, and perform various tasks. Understanding the anatomy and function of these muscles is essential for maintaining your horse's overall health and performance.
Muscles in horses serve various functions, including locomotion, posture maintenance, and heat production. The anatomy of horse muscles is complex, with each muscle having a specific role in the movement and stability of the horse. Proper conditioning and training are crucial to keeping these muscles strong and flexible.
Muscle injuries are common in horses, especially those involved in strenuous activities like racing or jumping. Common muscle injuries include strains, tears, and inflammation. Treatment for muscle injuries usually involves rest, cold therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, physical therapy and rehabilitation may be necessary to aid in the healing process.
Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate warm-up and cooldown routines can help prevent muscle injuries in horses. By understanding the importance of the muscular system and taking proper care of your horse's muscles, you can ensure their well-being and longevity.
Digestive System
With a specialized focus on the digestive system, your horse's ability to extract nutrients from food is vital for maintaining its overall health and performance. Understanding how the gut microbiome functions and how nutrient absorption occurs can help you optimize your horse's diet for peak performance and well-being.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Gut Microbiome: The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in your horse's digestive health. It consists of a diverse community of microorganisms that aid in breaking down food components, fermenting fiber, and synthesizing certain vitamins essential for your horse's well-being.
- Nutrient Absorption: The digestive system is responsible for absorbing essential nutrients from the food your horse consumes. Proper nutrient absorption ensures that your horse receives the necessary vitamins, minerals, proteins, and energy to support its bodily functions and performance.
- Gastric Ulcers: Horses are prone to developing gastric ulcers, especially in the upper digestive tract. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms associated with gastric ulcers can help you take preventive measures and provide appropriate care for your horse.
- Hindgut Fermentation: Hindgut fermentation is a vital process in your horse's digestive system where fiber is broken down by microbial fermentation in the cecum and colon. This process produces volatile fatty acids, which serve as an additional energy source for your horse.
Respiratory System
A healthy respiratory system in your horse is essential for optimal performance and overall well-being. Lung capacity plays a crucial role in your horse's ability to exchange gases efficiently. During exercise, the demand for oxygen increases, making efficient gas exchange vital for delivering oxygen to working muscles. Understanding your horse's breathing mechanics and respiratory rate can help you monitor its respiratory health.
Horses are obligate nasal breathers, meaning they primarily breathe through their nostrils. This unique feature allows for efficient filtration and humidification of the inspired air before it reaches the lungs. Your horse's respiratory rate can vary depending on various factors such as exercise intensity, environmental conditions, and overall health. Monitoring your horse's respiratory rate at rest and during exercise can provide valuable insights into its respiratory function.
Adequate lung capacity is essential for your horse to meet its oxygen demands during physical exertion. Regular exercise and conditioning can help improve your horse's lung capacity and overall respiratory efficiency. Maintaining a balanced respiratory system is crucial for ensuring your horse's well-being and performance. By understanding the importance of lung capacity, gas exchange, breathing mechanics, and respiratory rate, you can actively support your horse's respiratory health.
Circulatory System
Understanding how your horse's respiratory system interacts with its circulatory system is crucial for optimizing its performance and overall health. The circulatory system in your horse plays a vital role in maintaining its well-being by ensuring efficient blood flow, heart rate regulation, oxygen delivery, and nutrient distribution.
Here are four key points to help you grasp the importance of your horse's circulatory system:
- Blood flow: The circulatory system in your horse is responsible for the continuous circulation of blood throughout its body. This process ensures that oxygen and nutrients are transported to various tissues and organs, supporting their proper function.
- Heart rate: The heart rate of your horse is a critical component of its circulatory system. By regulating the heart rate, the circulatory system helps maintain an optimal flow of blood, ensuring that all parts of the body receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients.
- Oxygen delivery: Through the circulatory system, oxygen is transported from the lungs to the body's tissues, including muscles, to support energy production during physical activities.
- Nutrient distribution: Nutrients obtained from the digestive system are circulated by the blood to different parts of the body, providing essential building blocks for growth, repair, and overall health.
Nervous System
Efficient coordination of signals within your horse's body is essential for optimal performance and overall well-being. The nervous system plays a crucial role in this coordination, involving the brain function, spinal cord coordination, neuron communication, and sensory perception. The brain acts as the central command center, processing information received from various parts of the body and sending out signals for appropriate responses. This intricate organ controls everything from basic bodily functions to complex behaviors.
The spinal cord serves as a communication highway, relaying messages between the brain and the rest of the body. It's responsible for reflex actions and plays a vital role in coordinating movement. Neurons, the building blocks of the nervous system, transmit these signals through electrical and chemical impulses. This communication network enables your horse to react to its environment, communicate pain or discomfort, and regulate bodily functions.
Sensory perception is another critical aspect of the nervous system. Your horse's ability to sense its surroundings, feel touch, see, hear, and taste is all thanks to the intricate workings of this system. By interpreting sensory information, the nervous system helps your horse navigate its environment and interact with other animals and objects. Understanding and caring for your horse's nervous system is essential for ensuring its health and well-being.
Reproductive System
The reproductive system in horses plays a crucial role in their overall health and ability to produce offspring. Understanding the intricacies of their reproductive anatomy and physiology is essential for horse owners and breeders. Here are key points to consider:
- Breeding Behavior: Horses exhibit unique behaviors during breeding. Understanding these behaviors can help breeders identify the best time for mating and ensure successful reproduction.
- Reproductive Cycles: Female horses go through regular reproductive cycles, typically lasting around 21 days. Knowledge of these cycles is vital for managing breeding schedules and predicting fertility.
- Fertility Issues: Just like any other animal, horses can experience fertility issues that may impact their ability to reproduce. Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring are crucial to address any potential problems early on.
- Reproductive Health: Maintaining optimal reproductive health in horses is paramount for successful breeding. Proper nutrition, exercise, and hygiene play significant roles in ensuring the overall well-being of the horse's reproductive system.
Integumentary System
Your skin, hair, hooves, and glands collectively form the integumentary system in horses. The integumentary system serves various crucial functions in your horse's body. One primary function is skin protection. The skin acts as a barrier, protecting your horse from external elements such as UV radiation, pathogens, and physical injuries. It also helps regulate body temperature by controlling heat loss and preventing dehydration.
Hair growth is another essential aspect of the integumentary system. Horses have a unique coat of hair that provides insulation and protection. The hair follicles in the skin produce hair, which can vary in texture and color depending on the breed and individual characteristics of the horse. The hair coat helps repel water and insulate the body, keeping your horse warm in cold weather.
Hooves are also part of the integumentary system and play a crucial role in supporting your horse's weight and facilitating movement. The hoof wall, sole, and frog are specialized structures that protect the sensitive tissues within the hoof capsule. Proper hoof care is essential for maintaining your horse's overall health and soundness.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Horses Communicate With Each Other Through Body Language?
When horses communicate with each other through body language, they use various signals like ear position, tail movement, and facial expressions. Understanding equine behavior is key to interpreting these communication signals accurately.
In social interactions, horses rely on body language to convey their intentions and emotions, which play a significant role in herd dynamics. Observing these subtle cues can help you better understand how horses interact with each other and navigate their social hierarchy.
What Are Common Dental Issues That Horses May Face and How Are They Treated?
Taking care of your horse's teeth is crucial. Common dental issues like sharp points or uneven wear can lead to discomfort. Equine dentistry focuses on preventive care through regular check-ups.
Dental procedures such as floating help maintain proper tooth alignment and prevent issues. Good dental health is vital for your horse's overall well-being and can impact their ability to eat and perform.
Regular equine dental care is essential for maintaining your horse's health and happiness.
How Do Horses Regulate Their Body Temperature in Hot and Cold Weather?
To regulate body temperature in hot weather, horses rely on sweat evaporation to cool down. In cold weather, they use insulation to stay warm. This process is known as thermoregulation.
If it's really cold, horses may shiver to generate heat. So, whether it's sweltering or freezing, your horse's body has clever ways to keep its temperature just right.
What Is the Lifespan of a Horse in the Wild Versus in Captivity?
In the wild, horses usually live around 25-30 years, influenced by environmental factors like food availability and predators. In captivity, with proper care, they can live into their 30s or even 40s. Survival rates are higher in captivity due to protection from threats and access to consistent nourishment.
The difference in lifespan between wild and captive horses highlights the impact of their surroundings on longevity.
How Do Horses Form Social Hierarchies Within a Herd and How Do They Establish Leadership Roles?
Horses establish social hierarchies within a herd through dominance dynamics and communication strategies. By asserting themselves through body language, vocalizations, and subtle cues, they determine leadership roles. Dominant horses often control access to resources like food and water, while subordinates show respect through gestures like yielding.
These interactions help maintain order and minimize conflict within the group. Understanding these dynamics can enhance your appreciation of a horse's complex social structure.
Conclusion
Overall, a horse's anatomy and physiology are complex and fascinating.
From their skeletal system providing structure and support, to their muscular system enabling movement and power, each system plays a crucial role in their overall health and function.
Understanding these systems is key to proper care and management of horses, ensuring they live happy and healthy lives.
So next time you see a horse, remember all the intricate systems working together to make them the majestic creatures they are.