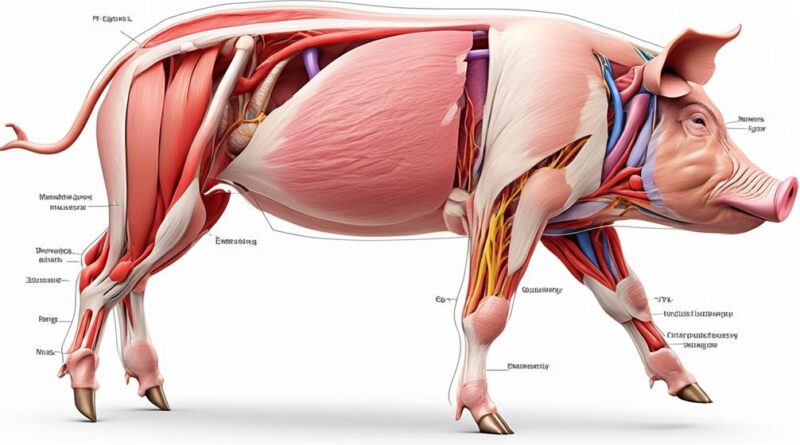
Essential Tips for Understanding Pig Muscular Anatomy
If you've ever dissected a pig in biology class, you probably found the muscular anatomy to be both fascinating and complex.
Understanding the essential tips for comprehending pig muscular anatomy can provide you with a deeper insight into the structure and function of these vital tissues.
From the basic structure of pig muscles to the comparison with human muscles, gaining a comprehensive understanding of pig muscular anatomy can shed light on various aspects that may surprise you.
Basic Structure of Pig Muscles
Understanding the basic structure of pig muscles is essential for gaining insight into their function and overall anatomy. Pig muscles, like human muscles, are composed of muscle fibers, connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. The muscle composition of pigs is similar to that of humans, with skeletal muscles being the most prominent. These muscles are responsible for the movement of the limbs, trunk, neck, and tail. Understanding the composition of pig muscles allows for a better grasp of the way they function and interact within the body.
When it comes to muscle movement, pigs rely on the contraction and relaxation of their muscles to perform various activities such as walking, running, and rooting. The movement of pig muscles is controlled by the nervous system, which sends signals to initiate muscle contractions. This coordinated muscle movement enables pigs to carry out essential tasks for their survival, such as foraging for food and escaping potential threats.
Additionally, understanding how pig muscles move is crucial for veterinarians and animal scientists in diagnosing and treating muscular injuries and disorders in these animals.
Muscle Groups in Pig Anatomy
Having grasped the basic structure of pig muscles, it's imperative to now explore the various muscle groups present in pig anatomy and their respective functions. Understanding the muscle groups and their functions will provide you with a comprehensive insight into the pig's muscular anatomy.
- Muscle Groups and Functions
- *Shoulder Muscles*: These muscles are responsible for providing support and mobility to the pig's front limbs, facilitating movements such as rooting and digging.
- *Back Muscles*: The back muscles play a crucial role in maintaining posture and providing stability to the spine, enabling the pig to carry out various physical activities.
- *Hamstring Muscles*: These muscles are vital for the pig's locomotion, as they contribute to the powerful thrust required for running and jumping.
- *Abdominal Muscles*: Responsible for core stability and support, the abdominal muscles are essential for maintaining the pig's body posture and balance.
- *Hind Leg Muscles*: These muscles are integral for the pig's propulsion and mobility, enabling activities such as walking, running, and climbing.
Understanding the muscle function and composition within these specific groups is essential for comprehending the pig's overall muscular anatomy. Each group of muscles plays a unique role in facilitating the pig's movements, stability, and overall physical well-being.
With this knowledge, you can gain a deeper understanding of how these muscles work together to support the pig's daily activities and overall health.
Understanding Muscle Fiber Types
To comprehend the intricate nature of pig muscular anatomy, it's essential to delve into the diverse types of muscle fibers present in their physiology. Understanding the types of muscle fibers and their composition is crucial in gaining insight into the functional capabilities of a pig's musculature.
Muscle fibers are classified into two main types: slow-twitch (Type I) and fast-twitch (Type II) fibers. Slow-twitch muscle fibers are primarily responsible for endurance activities. They contain a high concentration of mitochondria, which provides the energy required for sustained, low-intensity contractions. These fibers are rich in myoglobin, a protein that stores oxygen, enabling them to generate energy through aerobic metabolism.
On the other hand, fast-twitch muscle fibers are essential for rapid, powerful movements. They can be further subdivided into Type IIa and Type IIb fibers. Type IIa fibers possess characteristics of both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, making them suitable for activities that require both endurance and strength. Type IIb fibers, also known as fast glycolytic fibers, generate energy anaerobically and are well-suited for short bursts of intense activity.
The composition of muscle fibers in a pig's anatomy determines its physical abilities and influences the quality of meat. Different cuts of pork may contain varying proportions of these muscle fiber types, affecting factors such as tenderness and flavor. By understanding the nuances of muscle fiber types, pig farmers and those involved in the pork industry can make informed decisions regarding breeding, feeding, and meat processing techniques.
Functions of Pig Muscles
The diverse types of muscle fibers present in a pig's physiology directly influence its physical capabilities and the quality of its meat. Understanding the functions of pig muscles can provide valuable insights into their role in the animal's movement and meat quality.
- Muscle Contraction and Energy Production: Pig muscles are essential for movement and the performance of various activities. Muscle contraction allows pigs to carry out essential tasks such as walking, running, and even simple actions like eating and breathing. Additionally, muscle fibers play a crucial role in the production and storage of energy, ensuring that pigs have the necessary stamina to sustain their daily activities.
- Muscle Flexibility and Range of Motion: The flexibility and range of motion in pig muscles are vital for their overall mobility and agility. Flexible muscles enable pigs to bend, stretch, and move their limbs freely, contributing to their ability to navigate different terrains and environments. This flexibility also impacts the texture and tenderness of the meat, making it an important factor in the overall quality of pork products.
Understanding these functions of pig muscles sheds light on the importance of maintaining their health and well-being. By supporting muscle function through appropriate nutrition and care, farmers can contribute to the overall welfare and productivity of pigs while also enhancing the quality of pork for consumers.
Importance of Muscle Conditioning
Improving muscle conditioning in pigs is essential for enhancing their overall strength and agility. Just like in humans, muscle strength is crucial for pigs to perform daily activities, such as walking, running, and even standing. Muscle conditioning plays a vital role in the overall health and well-being of pigs, impacting their ability to thrive in various environments. By understanding exercise physiology in pigs, you can tailor their conditioning to ensure optimal muscle development.
Muscle conditioning directly impacts the strength and endurance of pigs. Through regular and appropriate physical activity, pigs can develop stronger and more resilient muscles. This is especially important for commercial pigs raised for meat production, as stronger muscles can contribute to improved meat quality and yield. Additionally, well-conditioned muscles can enhance a pig's ability to forage for food, explore their surroundings, and engage in natural behaviors, ultimately improving their welfare.
Understanding exercise physiology in pigs is crucial for designing effective conditioning programs. By incorporating a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups, you can promote balanced muscle development and overall fitness. Furthermore, proper muscle conditioning can help prevent injuries and musculoskeletal issues in pigs, ensuring their long-term health and functionality.
Common Pig Muscle Injuries
Enhancing muscle conditioning in pigs is essential for preventing and addressing common pig muscle injuries that can impact their overall strength and agility. It's important to be aware of the common pig muscle injuries and the best practices for injury prevention and rehabilitation techniques.
Common Pig Muscle Injuries
- Strains and Sprains: Pigs are susceptible to strains and sprains, especially in the legs and back muscles, which can occur during sudden movements or overexertion.
- Tendon Injuries: Tendon injuries can occur due to repetitive stress or overuse, particularly in the limbs and hooves of pigs.
- Muscle Tears: Pigs can experience muscle tears, often in the hamstrings or shoulder muscles, which may result from sudden acceleration or deceleration.
- Bruising: Pigs can develop bruises from minor injuries, such as bumping into objects or roughhousing with other pigs.
- Overexertion: Pigs can overexert themselves, leading to muscle fatigue and potential injuries, especially during intense physical activities.
To prevent these common pig muscle injuries, it's crucial to provide appropriate warm-up and cool-down exercises, maintain a balanced diet to support muscle health, and avoid overworking the pigs. Additionally, rehabilitation techniques such as physical therapy, massage, and controlled exercise can aid in the recovery of injured muscles.
Exploring Pig Muscle Development
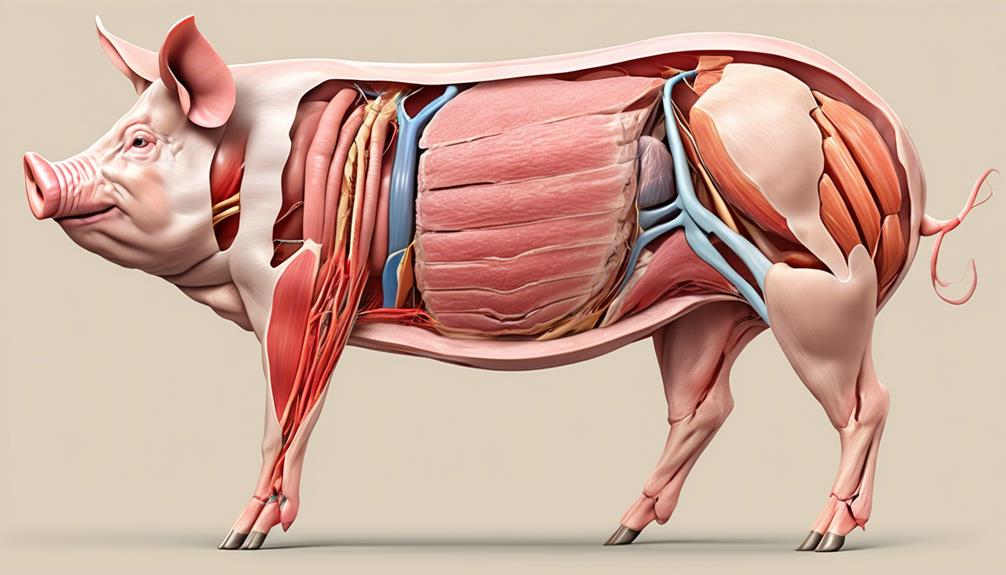
Exploring how pig muscle develops as they grow and mature is crucial for understanding their physical capabilities and overall health. Pigs go through different growth stages, each impacting their muscular development. Understanding these stages is essential for ensuring proper care and management of pigs.
From birth to market weight, pigs undergo significant muscle formation and growth. During the early stages, adequate nutritional requirements are crucial for supporting muscle development. Proper nutrition supports the formation of lean muscle mass, which is essential for the pig's overall health and productivity.
As pigs grow, their muscular development progresses, and they require specific nutrients to support this growth. Proteins, amino acids, and vitamins play a critical role in muscle formation. Ensuring that pigs receive a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs is vital for their muscle development. Additionally, providing a suitable environment for exercise and movement can further enhance muscle development in pigs.
Understanding the intricacies of pig muscle development can also aid in identifying and addressing any issues that may arise during the growth process. Monitoring the pig's physical development and adjusting their diet and environment as needed can help ensure optimal muscle formation and overall health.
Comparing Pig Muscles to Human Muscles
When comparing pig muscles to human muscles, it's evident that both share similarities in terms of structure and function. Understanding the composition, similarities, and differences between pig and human muscle tissues is crucial for various practical applications in veterinary medicine and agriculture.
- Composition: Both pig and human muscles are composed of muscle fibers, connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. The arrangement and distribution of these components contribute to the overall function and movement of the muscles in both species.
- Similarities and Differences: Pig and human muscles have similar types of muscle fibers, such as slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, which are responsible for different types of muscle contractions. However, there are also differences in the distribution and proportion of these fibers, influencing the strength and endurance capabilities of the muscles in each species.
- Practical Application in Veterinary Medicine: Understanding the similarities and differences between pig and human muscles is essential for veterinarians when diagnosing and treating muscle-related conditions in both pigs and humans. It allows for better insights into potential treatment approaches and rehabilitation strategies.
- Practical Application in Agriculture: In the context of agriculture, knowing the similarities and differences between pig and human muscles is crucial for meat quality assessment and production. It influences breeding programs, feeding strategies, and the development of specific cuts of meat to meet consumer demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Muscular Anatomy of Pigs Compare to Other Animals, Such as Cows or Horses?
When comparing pig muscular anatomy to other animals like cows or horses, you'll notice anatomical differences in muscle development. Understanding these variations is crucial for nutritional and farming purposes, helping you make informed decisions.
What Are the Best Practices for Preventing Muscle Injuries in Pigs During Farming or Handling?
To prevent muscle injuries in pigs during farming or handling, use proper preventive measures and farming techniques. Implement regular exercise, provide a balanced diet, and ensure comfortable housing. Minimize stress and avoid rough handling to maintain pig muscular health.
Can Muscle Conditioning in Pigs Affect the Taste or Quality of the Meat?
Regular exercise can impact the taste and quality of pig meat. Muscle conditioning affects the texture and flavor of the meat. So, it's essential to consider muscle quality when conditioning pigs for optimal meat taste and quality.
Are There Any Specific Differences in Muscle Fiber Types Between Different Pig Breeds?
When it comes to pig breeds, there are specific differences in muscle fiber composition. Different breeds exhibit variations in the distribution of fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle fibers, influencing meat quality and texture.
How Does Age and Diet Affect the Development and Growth of Pig Muscles?
Age-related changes in pig muscles can affect muscle mass and composition. Dietary influences play a significant role in muscle development and growth. Proper nutrition and management practices are essential for optimizing the muscular anatomy of pigs.
Conclusion
Now that you have a better understanding of pig muscular anatomy, you can apply this knowledge to improve your pig's overall health and performance.
By focusing on muscle conditioning, preventing injuries, and understanding muscle development, you can ensure that your pig stays strong and healthy.
Keep these essential tips in mind as you continue to care for and work with your pig.