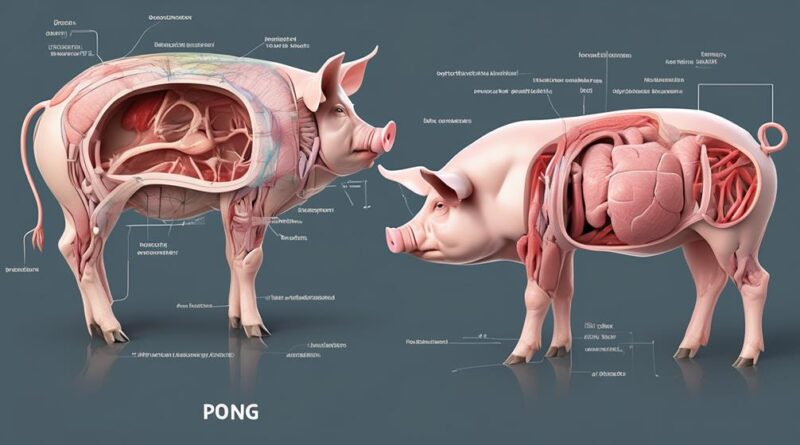
Exploring Pig Anatomy: An In-Depth 8-Point Breakdown
Coincidentally, have you ever wondered about the intricate details of pig anatomy? From the external features to the sensory organs, exploring the anatomy of a pig can provide a fascinating insight into the complexities of these animals.
As you delve into each point of our in-depth breakdown, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how the various systems work together to support the life of a pig.
So, are you ready to uncover the inner workings of these fascinating creatures and gain a new perspective on their anatomy?
External Features
When observing a pig's external features, you'll notice its distinct snout, compact body, and short legs. The pig's skin is covered in bristly hair, which can vary in color and texture depending on the breed. Their hooves are cloven, consisting of two main toes that aid in their stability and traction. The pig's external body features serve various functions essential to its survival.
Pig skin is an important organ that serves as a protective barrier against external elements and regulates body temperature. The hair that covers the pig's skin provides insulation and protection from the sun, insects, and minor scrapes or cuts. Additionally, the pig's hair can come in different colors and patterns, ranging from solid black to pink with spots.
The anatomy of a pig's hooves is designed to support its weight and provide stability while moving. The tough and durable nature of the hooves allows pigs to navigate various terrains, including mud and rough surfaces, with ease. Moreover, the pig's hooves play a crucial role in its overall mobility and agility.
Pigs also exhibit unique external body markings, such as spots, stripes, or solid colors, which can vary widely among different breeds. These distinctive markings often serve as identification and can differ significantly from one pig to another.
Understanding the external features of a pig is vital for proper care and management, as it provides insights into their physical abilities, environmental adaptations, and individual characteristics.
Skeletal System
Exploring the pig's skeletal system reveals its remarkable structure and role in supporting movement and bodily functions. The bone structure of pigs is similar to that of humans, with long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones making up their skeleton. These bones provide the framework for the pig's body, protecting its internal organs and providing attachment points for muscles.
The joints in a pig's skeletal system allow for smooth and coordinated movement. When examining joint movement, you'll notice that pigs have a variety of joint types, including hinge joints in their elbows and knees, ball-and-socket joints in their hips, and pivot joints in their necks, allowing for a wide range of motion.
Understanding the bone structure of pigs is essential for comprehending their physical capabilities and limitations. Pigs have a similar skeletal system to humans, with bones that are adapted to support their body weight and facilitate movement. The joint movement in pigs is crucial for their agility and flexibility. By having different types of joints, pigs can perform a diverse range of movements, from running and jumping to rooting and digging.
The skeletal system plays a fundamental role in the overall physiology and behavior of pigs, making it a vital area of study for anyone interested in understanding these fascinating animals.
Digestive System
The pig's digestive system efficiently processes food to extract essential nutrients for its growth and sustenance. As food enters the pig's mouth, it begins its journey through the digestive tract. Digestion commences in the mouth, where digestive enzymes in the saliva start breaking down carbohydrates.
From there, the food moves to the stomach, where it encounters powerful acids and digestive enzymes that further break down proteins and fats. The partially digested food then enters the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. Here, digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver aid in breaking down and absorbing nutrients such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
In addition to the pig's own digestive enzymes, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in the digestive process. The gut microbiome consists of a complex community of microorganisms that aid in the fermentation process. These microbes help break down fibers and other complex molecules that the pig's own digestive enzymes can't fully process.
Through this fermentation process, the gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids and other beneficial by-products that contribute to the pig's overall health.
Respiratory System
As you consider the pig's efficient digestive system, the next aspect to focus on is its respiratory system, which is crucial for the pig's overall health and well-being.
The respiratory system of a pig is similar to that of humans, consisting of the pig's lungs, airways, and breathing mechanism. Here's what you need to know about the pig's respiratory system:
- Respiratory System Structure: The pig's respiratory system includes the nasal passages, trachea, bronchial tubes, and lungs. These organs work together to ensure the pig receives an adequate supply of oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.
- Pig Lungs: Just like humans, pigs have a pair of lungs responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during the breathing process. The lungs are vital for the pig's survival, as they facilitate the oxygenation of the blood, which is necessary for cellular respiration.
- Breathing Mechanism: Pigs breathe through their nostrils, and the air travels through the nasal passages into the trachea, then into the bronchial tubes, and finally into the lungs. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle at the base of the chest, plays a crucial role in the pig's breathing process. When the pig inhales, the diaphragm contracts, allowing the lungs to expand and draw in air. Conversely, when the pig exhales, the diaphragm relaxes, causing the lungs to expel air.
Understanding the intricacies of the pig's respiratory system is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of these animals.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system in pigs efficiently transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout their bodies, playing a crucial role in maintaining their overall health and vitality. Blood circulation in pigs is facilitated by a complex network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart, a muscular organ, serves as the central pump of this circulatory system. It contracts and relaxes rhythmically to propel the blood throughout the body.
Pigs have a four-chambered heart, similar to humans, which allows for efficient separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle, which then sends the blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart, entering the left atrium and then the left ventricle, which pumps it back out to the body through the aorta.
The heart's function is vital for sustaining life, as it ensures a continuous flow of blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. This process supports the pig's metabolic needs and aids in maintaining overall health. Understanding the intricacies of the circulatory system in pigs is essential for proper animal care and management.
Reproductive System
Efficient reproduction in pigs requires careful management and understanding of their reproductive system. The reproductive system of a pig is complex and plays a crucial role in ensuring successful breeding and production. Here are three key aspects to consider when exploring the reproductive system of pigs:
- Hormonal Regulation: The reproductive system in pigs is intricately regulated by various hormones. Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) play pivotal roles in the estrous cycle, follicular development, ovulation, and maintenance of pregnancy. Understanding the hormonal regulation of the reproductive system is essential for successful breeding and reproduction management in pig farming.
- Reproductive Cycles: Pigs have a unique reproductive cycle characterized by the estrous cycle, which lasts around 21 days. During this cycle, female pigs go through different phases, including proestrus, estrus, metestrus, and diestrus. It's crucial for pig farmers to be familiar with these reproductive cycles to optimize breeding programs and ensure efficient reproduction.
- Breeding Management: Proper understanding of the pig's reproductive system is vital for effective breeding management. This includes timing the insemination or mating process, monitoring heat signs, and ensuring optimal conditions for successful conception and pregnancy. By comprehensively understanding the reproductive system and its cycles, pig farmers can enhance breeding efficiency and overall reproductive success.
Understanding the hormonal regulation and reproductive cycles of pigs is fundamental for successful breeding and reproduction management. By applying this knowledge, pig farmers can optimize their breeding programs and ensure efficient reproduction within their herds.
Nervous System
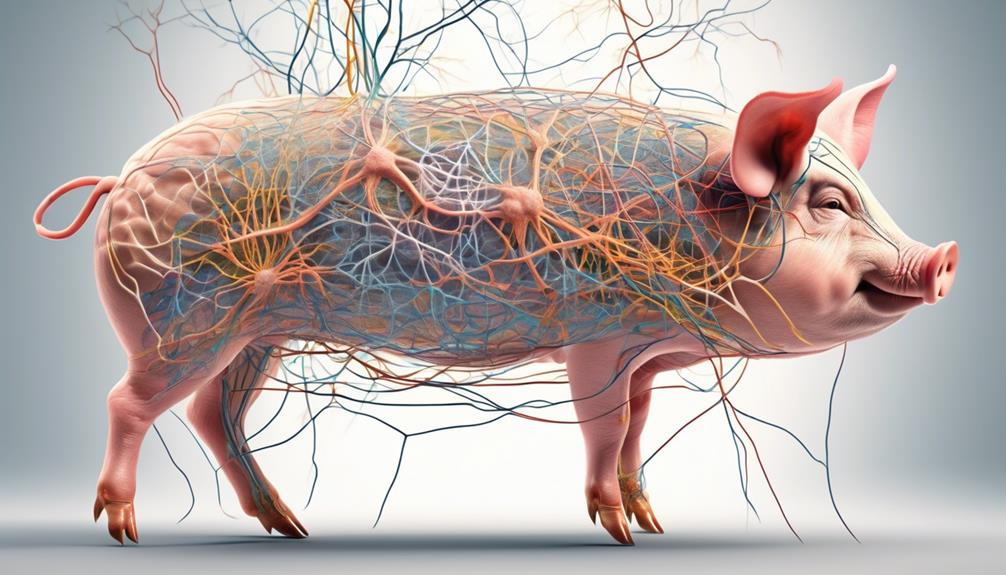
Wondering how the nervous system of pigs influences their behavior and physiological responses? Well, let's dive into it.
The nervous system of pigs, much like in humans, consists of two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The central nervous system of pigs, which includes the brain and spinal cord, plays a crucial role in processing information and coordinating responses. The pig's brain is responsible for higher functions such as learning, memory, and decision-making, while the spinal cord serves as a pathway for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. This intricate network allows pigs to react to various stimuli and adapt to their environment.
On the other hand, the peripheral nervous system of pigs consists of nerves that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body. These nerves act as communication lines, relaying information from the external environment to the CNS and vice versa. For pigs, the PNS enables sensory experiences such as touch, taste, smell, and sound, as well as motor functions like movement and muscle coordination.
Sensory Organs
If you want to understand how pigs perceive the world around them, their sensory organs play a crucial role in processing external stimuli and relaying information to their nervous system. Pigs have well-developed sensory organs that enable them to interact with their environment effectively.
Here are some key aspects of a pig's sensory organs:
- Olfactory System: Pigs have an impressive sense of smell, thanks to their highly developed olfactory system. Their snouts are equipped with numerous olfactory receptors, allowing them to detect scents with incredible precision. This acute sense of smell not only helps pigs locate food but also plays a vital role in their social interactions and in identifying potential threats in their surroundings.
- Taste Buds: Just like humans, pigs have taste buds on their tongues that allow them to discern different flavors. Their sense of taste helps them distinguish between various food items, allowing them to make dietary choices based on flavor preferences. Additionally, their taste buds aid in identifying potentially harmful substances, contributing to their overall well-being.
- Sensory Hairs: Pigs have sensory hairs, or whiskers, located on different parts of their body, including their face. These sensory hairs are sensitive to touch, air currents, and vibrations, providing pigs with additional information about their surroundings and helping them navigate their environment with precision.
Understanding the sensory organs of pigs provides valuable insights into how they experience the world and adapt to their surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Most Common Breeds of Pigs Used for Research and Agriculture?
The most common breeds of pigs used for research and agriculture are Yorkshire, Landrace, and Duroc. They are popular for their adaptability, growth rate, and meat quality, making them valuable for scientific studies and commercial farming.
How Do Pigs Communicate With Each Other and What Types of Vocalizations Do They Make?
Pigs communicate through a variety of vocalizations, such as grunts, squeals, and snorts. They use these sounds to convey different emotions and needs. These communication methods play a crucial role in their social interactions and behavioral patterns.
What Is the Average Lifespan of a Domestic Pig in Different Environments?
In different environments, domestic pigs typically live for 10-15 years. Factors like diet, healthcare, and living conditions influence their lifespan. Pigs raised for meat usually have shorter lives than those kept as pets or in sanctuaries.
Do Pigs Have Any Unique Behaviors or Social Structures That Are Distinct From Other Animals?
Pigs exhibit unique behaviors and social structures. They are highly social animals, forming strong bonds within their groups. They communicate through various sounds and body language, and even demonstrate problem-solving abilities, making them fascinating creatures to observe.
Are There Any Ethical Concerns or Controversies Surrounding the Use of Pigs in Scientific Research or Agriculture?
There are ethical concerns and research controversies surrounding the use of pigs in scientific research and agricultural practices. Animal welfare is a central issue, with debates on proper treatment and the impact of farming methods.
Conclusion
Now that you've explored the anatomy of a pig in detail, you have a better understanding of its external and internal features.
From the skeletal and digestive systems to the reproductive and nervous systems, you've gained insight into the complexity of pig anatomy.
Whether you're studying veterinary science or simply curious about animal biology, this breakdown has provided valuable information on the intricacies of pig anatomy.
Keep exploring and learning about the fascinating world of animal anatomy!